

For example, you have made your shopping list on which you have mentioned various items such as chocolates, milk, cheese, eggs, and toothpaste.
#SERIAL POSITION EFFECT SERIAL#
The serial position effect is a psychological phenomenon in which an individual is more likely to remember the first and last items of the list than the middle items. Can We Avoid the Serial Position Effect?.
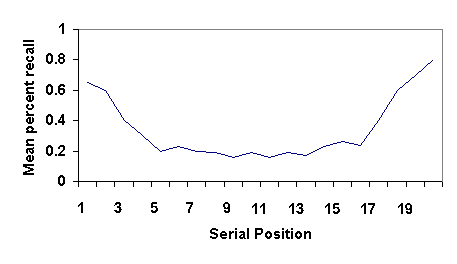 Real-life Examples of Serial Position Effect. The publisher and the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to persons or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content or advertisements. The appearance of advertisements or/and product references in the publication is not a warranty, endorsement, or approval of the products or services advertised or of their effectiveness, quality or safety. This is particularly important when the recommended agent is a new and/or infrequently employed drug.ĭisclaimer: The statements, opinions and data contained in this publication are solely those of the individual authors and contributors and not of the publishers and the editor(s). However, in view of ongoing research, changes in government regulations, and the constant flow of information relating to drug therapy and drug reactions, the reader is urged to check the package insert for each drug for any changes in indications and dosage and for added warnings and precautions. No part of this publication may be translated into other languages, reproduced or utilized in any form or by any means, electronic or mechanical, including photocopying, recording, microcopying, or by any information storage and retrieval system, without permission in writing from the publisher.ĭrug Dosage: The authors and the publisher have exerted every effort to ensure that drug selection and dosage set forth in this text are in accord with current recommendations and practice at the time of publication. Conclusion: Analyses of the serial position effect may be a useful complement to clinical neuropsychological measures for distinguishing amnestic MCI patients from normal aging and patients with different stages of dementia.Ĭopyright: All rights reserved. The serial position profile of nonamnestic MCI patients resembled that of healthy control subjects, whereas amnestic MCI patients showed poorer performance in all 3 positions but no significant difference as a function of serial word position. Results: With progression of dementia, memory deficits increased and the impairment in the primacy effect during the learning trials advanced, whereas the recall of recent items was less impaired.
Real-life Examples of Serial Position Effect. The publisher and the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to persons or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content or advertisements. The appearance of advertisements or/and product references in the publication is not a warranty, endorsement, or approval of the products or services advertised or of their effectiveness, quality or safety. This is particularly important when the recommended agent is a new and/or infrequently employed drug.ĭisclaimer: The statements, opinions and data contained in this publication are solely those of the individual authors and contributors and not of the publishers and the editor(s). However, in view of ongoing research, changes in government regulations, and the constant flow of information relating to drug therapy and drug reactions, the reader is urged to check the package insert for each drug for any changes in indications and dosage and for added warnings and precautions. No part of this publication may be translated into other languages, reproduced or utilized in any form or by any means, electronic or mechanical, including photocopying, recording, microcopying, or by any information storage and retrieval system, without permission in writing from the publisher.ĭrug Dosage: The authors and the publisher have exerted every effort to ensure that drug selection and dosage set forth in this text are in accord with current recommendations and practice at the time of publication. Conclusion: Analyses of the serial position effect may be a useful complement to clinical neuropsychological measures for distinguishing amnestic MCI patients from normal aging and patients with different stages of dementia.Ĭopyright: All rights reserved. The serial position profile of nonamnestic MCI patients resembled that of healthy control subjects, whereas amnestic MCI patients showed poorer performance in all 3 positions but no significant difference as a function of serial word position. Results: With progression of dementia, memory deficits increased and the impairment in the primacy effect during the learning trials advanced, whereas the recall of recent items was less impaired. 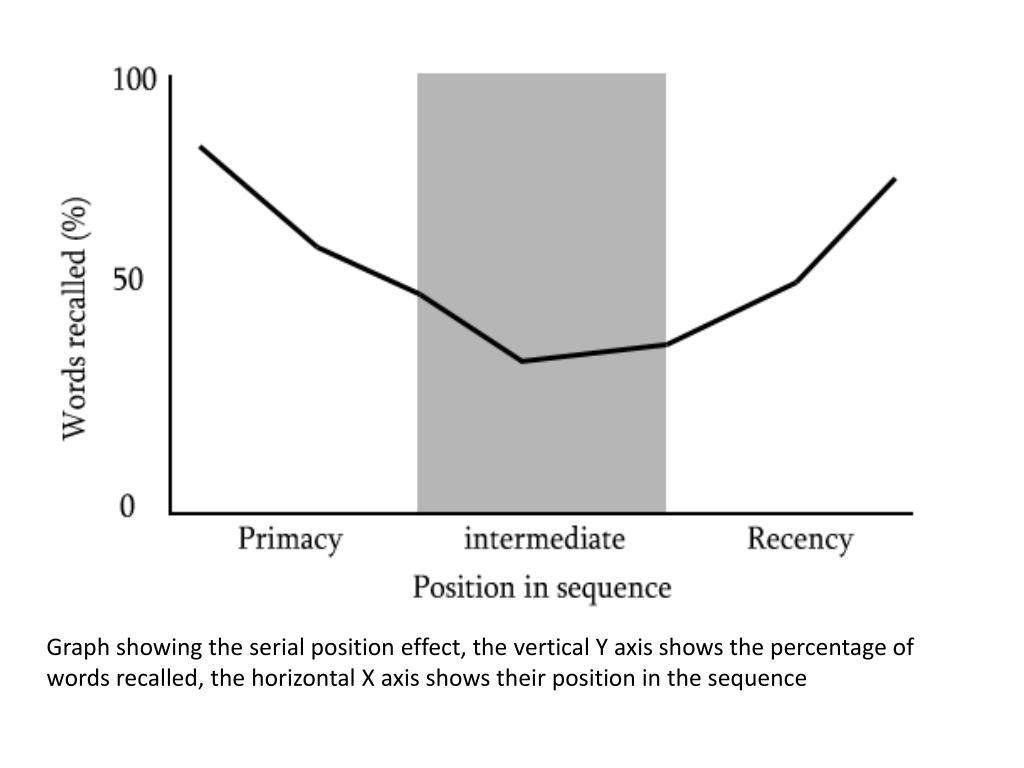
Methods: The serial position effects was tested with the CERAD word list task in 184 persons (39 healthy control subjects, 15 amnestic MCI single domain subjects, 23 amnestic MCI multiple domain subjects, 31 nonamnestic MCI subjects, 45 early or mild AD patients, and 31 moderate AD patients).
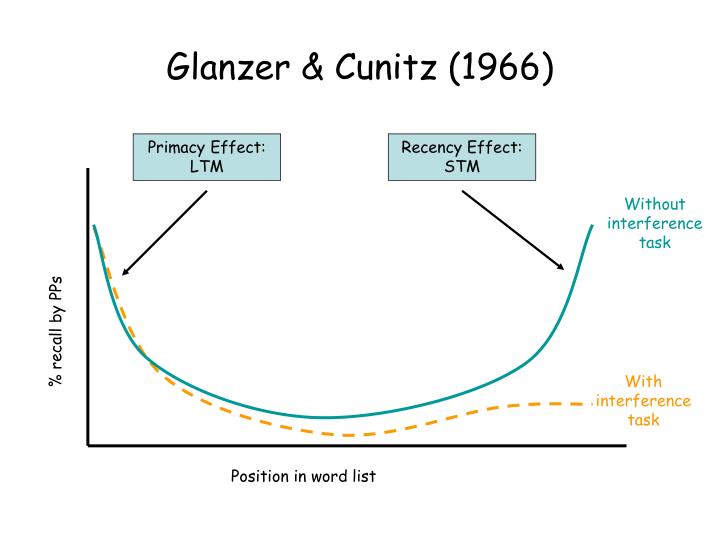
Background/Aims: This study aimed to investigate whether the serial position effects in memory can differentiate patients with different subtypes of mild cognitive impairment (MCI) from healthy controls and patients with different stages of Alzheimer's disease (AD).








 0 kommentar(er)
0 kommentar(er)
